
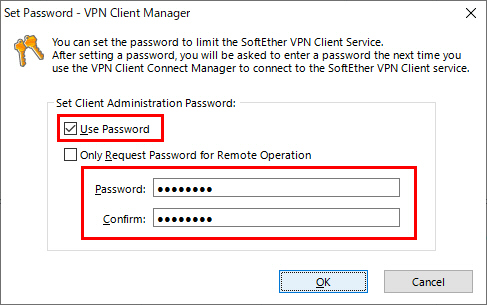
Here are step-by-step guides for that: Require MFA for administrators. Security defaults is mandatory for all partners MFA requirement.

Create equivalent conditional access policies for the baseline you used to have. It’s usually located at /etc/nginx/nf, /etc/nginx/sited-enabled/ (Ubuntu / Debian) or /etc/nginx/conf.d/nf (RHEL / CentOS). Here's what you have to do: Turn off Security Defaults - Azure AD -> Properties - Manage Security Defaults -> Enable Security Default - OFF.
ENABLE SECURITY DEFAULTS UPDATE
Header always set Referrer-Policy "strict-origin-when-cross-origin"įor nginx, you’ll have to update the configuration file. Just blocking a few file types is not enough. It’s pretty easy to turn on and shouldn’t have any user impact. Default setting: Disabled Recommended Setting: Enabled. Header always set Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'" Best Attachments setting for Microsoft Office 365 Email Security. Header always set X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" Header always set X-XSS-Protection "1 mode=block" Header always set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000" Apache Security headersįor Apache, you’ll need to update your configuration to include the correct header directives.Īdd this to the virtual host configuration in /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/nf or /etc/httpd/sites-enabled/nf: To configure your webserver, you can apply the settings described below - for Apache, Nginx, and HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS). Webserver Configuration (Apache, Nginx, and HSTS)
For example, they modify the behavior of web browsers to avoid security vulnerabilities just to accept one kind of valid server certificate like TLS. They are directives to increase the protection and create more defense against vulnerabilities using browsers. CVSS Vector: AV:N/AC:H/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:L/I:L/A:N What are Security headers?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
